Under the entry age normal (EAN) cost method, normal cost (NC) is determined as a level percentage of salary, or a level dollar amount, over a participant’s career. The accrued liability (AL) is determined as the excess of the present value of future benefits (PVB) over the present value of future normal costs (PVFNC). That is,
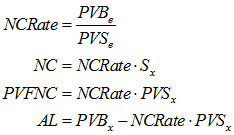
Where:
![]() is the present value of future benefits at entry
is the present value of future benefits at entry
![]() is the present value of future benefits at the valuation date
is the present value of future benefits at the valuation date
![]() is the present value of future salary, or service (if level dollar NC), at entry
is the present value of future salary, or service (if level dollar NC), at entry
![]() is the present value of future salary, or service (if level dollar NC), at the valuation date
is the present value of future salary, or service (if level dollar NC), at the valuation date
![]() is the valuation salary, or 1 (if level dollar NC), for the year beginning on the valuation date
is the valuation salary, or 1 (if level dollar NC), for the year beginning on the valuation date
The end of the entry age normal funding span, or the last age to compute a normal cost, is determined separately for each benefit (i.e., Benefit Definition) and is specified under the Liability Methods topic of funding Valuation Assumptions.
To compute employer contributions using the entry age normal method, first select an entry age normal liability method under the Liability Methods topic of funding Valuation Assumptions and run a Valuation or Core Projection. Then select an entry age normal cost method under the Contribution Policy topic of the Asset & Funding Policy and run a Valuation Set, Deterministic Forecast or Stochastic Forecast.
Alternative Benefit Formula for EAN Normal Cost
In the pension modes except German and U.K., you can provide an alternative benefit formula for computing the EAN normal cost. The standard Benefit Formula is used for the calculation of PVBx, while the alternative benefit formula, if supplied, is used for calculating PVBe, which drives normal cost and the present value of future normal costs. Both formulas are entered as part of a Benefit Definition.
Examples:
-
A common use of the alternative benefit formula is to reflect an ultimate entry age normal cost method (sometimes called "entry age normal with replacement): the alternative formula for computing EAN normal cost would be the benefit formula applicable for a new entrant hired today. The grandfathered benefits will still be reflected in PVB, will have no impact on normal cost and PVFNC, and thus are reflected totally in the accrued liability.
-
For frozen plans having no future accruals, if you wish to generate a zero normal cost, specify an EAN normal cost benefit formula of zero. Then the entire liability will be considered to have accrued in the past and the EAN liability will equal the PVFB. Note: frozen benefit formulas with no future accruals will not generate a zero normal cost unless the EAN normal cost benefit formula is set to zero. This is because the EAN funding span for each benefit, as defined in Valuation Assumptions, must still apply.
To assist in checking results when using this technique, the Benefit Definition sample life report displays the calculation of both the standard benefit and any alternative EAN normal cost basis benefit. Also, in the EAN liability and normal cost sample life report, the “PV of benefits at funding age” is based on the alternative formula.
Average Entry Age Normal technique
This variation of EAN, popular in some countries, is available in the universal pension mode. For this approach, a participant who is deemed to be typical must be chosen. Then for every participant having a normal cost (i.e., active, meeting the requirements to be included in liabilities but younger than the age at which retirement rates become 100% or younger than the last funding age, if earlier), the normal cost calculation is based on this “typical” participant’s normal cost rate (or dollar amount if a level dollar variation of entry age normal was selected).
The parameter to apply the average EAN technique is found under the Liability Methods topic of funding Valuation Assumptions. A database file and a selection expression that results in the selection of a single record must then be entered. To assist in checking results when using this technique, the EAN normal cost development in sample lives is based on the record specified in the Valuation Assumptions.
In a Core Projection, the unique normal cost rate (or dollar amount) will be used in all years. It will remain unchanged even if there are plan amendments.