The Mortality Rates library defines the mortality rates needed to calculate Annuity Factors and Actuarial Equivalence. The Mortality Rates Library has two general types of mortality tables: standard and dynamic. If you are creating a new table, the New button, via the drop-down arrow, allows you to select Standard or Dynamic, where the default is to create a standard mortality table. Creating Dynamic Mortality tables are discussed at the end of this article and dynamic mortality in general is discussed in Dynamic Mortality.
Mortality rates are entered through the same (table) interface as benefit component and payment form conversion tables, and that interface is shared with ProVal. As such, there are some options that may be used to create a table that either will not be permitted for a calculation or that will be ignored during a calculation. For example, while many additional options for table creation are technically available, the mortality rates may vary only by age, sex and year of birth, and you may apply improvement scales. Many standard tables are automatically included in each ProAdmin (and ProVal) client. While some of these vary between pre- and post-commencement, ProAdmin only recognizes and reflects post-commencement mortality rates. See Table Interface for details about constructing tables and entering their values.
The following mortality tables are automatically included in an existing ProAdmin client, when the client files are updated, and in every new ProAdmin client. (Other mortality tables may be added in the future.) The tables may be hidden from the current Project; click the Unhide button to gain access. You cannot erase, or save changes to, mortality tables that are automatically included in a ProAdmin client. The tables currently available are:
- Society of Actuaries ("SOA") tables:
- 1971 Group Annuity Mortality Table;
- 1983 Group Annuity Mortality Table;
- 1994 Group Annuity Mortality Static Table;
- RP-2000 Combined Mortality Table;
- RP-2000+ Combined Mortality Table (dynamic) – the male and female mortality rates from the (static) RP-2000 Combined Mortality Table projected to the valuation year using Scale AA, updated automatically – see the discussion of dynamic mortality at the end of this article;
- RP-2014 Adjusted to 2006 [x] Mortality (base rates only), where [x] refers to one of the following population subsets:
- Blue Collar,
- Disabled Retiree,
- White Collar, or
- Total Dataset;
- RP-2014 [x] Mortality with Scale MP-2014, where [x] refers to the same subsets above;
- RPH-2014 Adjusted to 2006 [x] Headcount-weighted Mortality (base rates only), where [x] refers to the same subsets above;
- RPH-2014 [x] Headcount-weighted Mortality with Scale MP-2014, where [x] refers to the same subsets above;
- UP-1984 (1984 Unisex Pensioner) Mortality;
- UP-1994 (1994 Uninsured Pensioner) Mortality;
- UP-1994 Mortality with Projection Scale AA;
- UP-1994 Projected to 2015 with Projection Scale AA;
- U.S. Internal Revenue Service ("IRS") tables (see Dynamic Mortality for details regarding dynamic mortality tables which update automatically):
- 1983 GAM (Group Annuity Mortality) per Revenue Ruling 95-28 - male and female tables specified for current liability calculations for U.S. qualified plans by IRS Revenue Ruling 95-28
- 1995 Applicable Mortality Table - unisex table specified for U.S. qualified plans by IRS Revenue Ruling 95-6 for computations under IRC Sections 415 and 417
- Applicable Mortality Table per Revenue Ruling 2001-62 - unisex table specified in IRS Revenue Ruling 2001-62, to replace the table specified in IRS Revenue Ruling 95-6, for computations under IRC Sections 415 and 417 for U.S. qualified plans
- 2007 Current Liability Combined Mortality - male and female optional combined tables specified for current liability calculations for U.S. qualified plans by IRS Regulation 1.412(l)(7)-1, to replace the tables specified in Revenue Ruling 95-28
- 2008 Applicable Mortality Table - unisex table specified for U.S. qualified plans in IRS Revenue Ruling 2007-67 for computations under IRC Section 417 for 2008 plan years
- 2008 Generational Mortality - male and female non-annuitant and annuitant base tables and projection factors specified by IRS Regulation 1.430(h)(3)-1 for present value determination under PPA funding rules for U.S. qualified plans
- 2008 Small Plan Combined Static Mortality - male and female optional combined static tables specified for present value determination, under PPA funding rules for U.S. qualified plans, by IRS Regulation 1.430(h)(3)-1 with respect to valuation dates occurring in 2008
- 2008 Static Mortality - male and female non-annuitant and annuitant static tables specified for present value determination, under PPA funding rules for U.S. qualified plans, by IRS Regulation 1.430(h)(3)-1 with respect to valuation dates occurring in 2008
- 2008+ Applicable Mortality Table for 417(e) (dynamic) - unisex table specified for U.S. qualified plans in IRS Revenue Ruling 2007-67
- 2008+ Applicable Mortality Table for 417(e), 0 Pre-Commencement (dynamic) - unisex mortality rates from the "IRS 2008+ Applicable Mortality Table for 417(e) (dynamic)" described above, applied at ages after annuity commencement only (these rates will be displayed in the post-commencement column), with zero mortality rates at all ages prior to annuity commencement (rates of zero will be displayed in the pre-commencement column)
- 2008+ Small Plan Combined Static Mortality (dynamic) - male and female optional combined static tables specified for present value determination, under PPA funding rules for U.S. qualified plans, by IRS Regulation 1.430(h)(3)-1; updated automatically
- 2008+ Small Plan Combined Static Mortality, 0 Pre-Commencement (dynamic) - male and female mortality rates from the “IRS 2008+ Small Plan Combined Static Mortality (dynamic)” described above, applied at ages after annuity commencement only (these rates will be displayed in the post-commencement columns), with zero mortality rates at all ages prior to annuity commencement (rates of zero will be displayed in the pre-commencement
- 2008+ Static Mortality (dynamic) - male and female non-annuitant and annuitant static tables specified for present value determination, under PPA funding rules for U.S. qualified plans, by IRS Regulation 1.430(h)(3)-1
- 2008+ Static Mortality, 0 Pre-Commencement (dynamic) - male and female mortality rates from the “IRS 2008+ Static Mortality (dynamic)” described above, applied at ages after annuity commencement only (these rates will be displayed in the post-commencement columns), with zero mortality rates at all ages prior to annuity commencement (rates of zero will be displayed in the pre-commencement columns)
- 2018 Generational Mortality - male and female non-annuitant and annuitant base tables and projection factors specified by IRS Regulation 1.430(h)(3)-1 for present value determination under PPA funding rules for U.S. qualified plans with valuation dates on or after 1/1/2018
- 2018+ Applicable Mortality Table for 417(e) (dynamic) - unisex table specified for U.S. qualified plans in IRS Revenue Ruling 2017-60
- 2018+ Applicable Mortality Table for 417(e), 0 Pre-Comm (dynamic) - unisex mortality rates from the "IRS 2018+ Applicable Mortality Table for 417(e) (dynamic)" described above, applied at ages after annuity commencement only (these rates will be displayed in the post-commencement column), with zero mortality rates at all ages prior to annuity commencement (rates of zero will be displayed in the pre-commencement column)
- 2018+ Small Plan Combined Static Mortality (dynamic) - male and female optional combined static tables specified for present value determination, under PPA funding rules for U.S. qualified plans, by IRS Regulation 1.430(h)(3)-1; updated automatically
- 2018+ Small Plan Combined Static Mortality, 0 Pre-Comm (dynamic) - male and female mortality rates from the “IRS 2018+ Small Plan Combined Static Mortality (dynamic)” described above, applied at ages after annuity commencement only (these rates will be displayed in the post-commencement columns), with zero mortality rates at all ages prior to annuity commencement (rates of zero will be displayed in the pre-commencement columns)
- 2018+ Static Mortality (dynamic) - male and female non-annuitant and annuitant static tables specified for present value determination, under PPA funding rules for U.S. qualified plans, by IRS Regulation 1.430(h)(3)-1
- 2018+ Static Mortality, 0 Pre-Comm (dynamic) - male and female mortality rates from the “IRS 2018+ Static Mortality (dynamic)” described above, applied at ages after annuity commencement only (these rates will be displayed in the post-commencement columns), with zero mortality rates at all ages prior to annuity commencement (rates of zero will be displayed in the pre-commencement columns)
- 2018-2019+(MP16-17) Applicable Mortality for 417(e) (dynamic) - unisex table specified for U.S. qualified plans in IRS Revenue Ruling 2017-60
- 2018-2019+(MP16-17) Applicable Mortality for 417(e), 0 Pre-Comm (dynamic) - unisex mortality rates from the "IRS 2018-2019+(MP16-17) Applicable Mortality for 417(e) (dynamic)" described above, applied at ages after annuity commencement only (these rates will be displayed in the post-commencement column), with zero mortality rates at all ages prior to annuity commencement (rates of zero will be displayed in the pre-commencement column)
- 2018-2019+(MP16-17) Small Plan Combined Static Mortality (dynamic) - male and female optional combined static tables specified for present value determination, under PPA funding rules for U.S. qualified plans, by IRS Regulation 1.430(h)(3)-1; updated automatically.
- 2018-2019+(MP16-17) Small Plan Combined Static Mortality, 0 Pre-Comm (dynamic) - male and female mortality rates from the “IRS 2018-2019+(MP16-17) Small Plan Combined Static Mortality (dynamic)” described above, applied at ages after annuity commencement only (these rates will be displayed in the post-commencement columns), with zero mortality rates at all ages prior to annuity commencement (rates of zero will be displayed in the pre-commencement columns)
- 2018-2019+(MP16-17) Static Mortality (dynamic) - male and female non-annuitant and annuitant static tables specified for present value determination, under PPA funding rules for U.S. qualified plans, by IRS Regulation 1.430(h)(3)-1
- 2018-2019+(MP16-17) Static Mortality, 0 Pre-Comm (dynamic) - male and female mortality rates from the “IRS 2018-2019+(MP16-17) Static Mortality (dynamic)” described above, applied at ages after annuity commencement only (these rates will be displayed in the post-commencement columns), with zero mortality rates at all ages prior to annuity commencement (rates of zero will be displayed in the pre-commencement columns)
- Canadian Institute of Actuaries ("CIA") tables:
The "IRS 2018-2019+(MP16-17)..." mortality tables use MP-2016 mortality improvement scale to calculate static tables for calculation dates before January 1, 2019, and MP-2017 to calculate static tables for calculation dates on or after January 1, 2019. There are additional tables in ProAdmin which follow the same methodology to develop the static tables for calculation dates in years 2020 through 2023. The names for each of these tables start with "IRS 2018-[applicable year]..."
The IRS changed the base mortality table on which mortality improvement scales will be applied for 2024 and years thereafter. ProAdmin will use the same naming convention that was used for the IRS issued tables from 2018 through 2023, but all tables will start with "IRS 2024+... Please see 2024+ Dynamic Mortality for more details.
The following tables are base rates only as published by the CIA Pension Experience Subcommittee February 2014 and do not have the improvement scale or any size adjustment factors built in.
- CPM-2014 Combined Mortality (base rates only)
- CPM-2014 Private Sector Mortality (base rates only)
- CPM-2014 Public Sector Mortality (base rates only)
The following tables are linked to the relevant base rates and include the applicable improvement scale. Note that size adjustment factors, as published by in the CIA Pension Experience Subcommittee February 2014, have been pre-filled in under the mortality linkage advanced parameters. If you wish to apply them, select the radio button to apply a database field adjustment factor, check the box to transform the values based on the spreadsheet provided. Because the table is protected, the resulting table with size adjustment factors must be saved under a new name.
- CPM-2014 Combined Mortality with CIA Scale CPM-B
- CPM-2014 Private Sector Mortality with CIA Scale CPM-B
- CPM-2014 Public Sector Mortality with CIA Scale CPM-B
- ERISA 4044 Table:
- ERISA 4044 Mortality (dynamic) - the male and female mortality rates from the (static) UP 1994 mortality table projected to ten years after the valuation year using Scale AA, updated automatically – see the discussion of dynamic mortality at the end of this article.?
Check the Link mortality base rates box if the mortality table you are building is a modification based on previously existing underlying tables. When you check the box, the spreadsheet values and Options button will become inaccessible; click the Parameters button to specify the linkage parameters.
In the Mortality Table Base Rate Linkage Parameters dialog box, select the Mortality table that Base rates are drawn from using the list of static mortality rate reference tables unhidden in the current Project. If a sex-distinct table has been selected, specify whether you want to Transform to unisex, blending specified weights. Enter the percentage weight of male rates, and the complementary percentage weight of female rates will populate. For example, you could create a new unisex mortality table that blends 80% of male and 20% of female rates from an existing mortality table.
You may shift base rates by a specified number of years, to reflect an Age setback, again separately for Male and Female rates. Note that a negative age setback will be applied instead as a set-forward. For example, a setback of -4 will set the base rate at age 40 equal to the original rate for age 44. For no age set back, enter 0. The table can be further adjusted with a multiplicative Adjustment factor separately for Male and Female rates. For no adjustment, enter 1. If the Age setback between male and female or the Adjustment factor between male and female are different, the resultant table will be sex-distinct.
When you click OK, to return to the Mortality Rate Table dialog box, the table you are building will populate with the newly-linked values. Note that you may uncheck the box if you wish to further modify the values or examine them in more detail.
Mortality Projection
Check the Apply Improvement Scale box to apply rates of annual improvement in mortality experience to the mortality base rates, to create either a fully generational table or a static table reflecting mortality improvement to a particular year (typically in the future, although you may specify a year in the past). While this section references Pre- and Post-Commencement improvement scales separately, ProAdmin only uses post-commencement mortality rates for its calculations.
Select a Pre-Commencement improvement scale from the list of scales available in ProAdmin’s Mortality Improvement Scales library, or click the ![]() button to access the library, in which you may create new improvement scales or modify existing ones. Enter the (pre-commencement) Base year (year from which you are projecting) in the text box. Similarly, select a Post-Commencement improvement scale, accessing the library by means of the
button to access the library, in which you may create new improvement scales or modify existing ones. Enter the (pre-commencement) Base year (year from which you are projecting) in the text box. Similarly, select a Post-Commencement improvement scale, accessing the library by means of the ![]() button if desired, and enter the (post-commencement) Base year. For Projection, select either Fully generational, to project mortality improvement indefinitely into the future, or To year, to project from the base year only to the specified year. See the Technical Reference article entitled Mortality improvement (generational mortality) for details about the calculation of projected mortality rates.
button if desired, and enter the (post-commencement) Base year. For Projection, select either Fully generational, to project mortality improvement indefinitely into the future, or To year, to project from the base year only to the specified year. See the Technical Reference article entitled Mortality improvement (generational mortality) for details about the calculation of projected mortality rates.
If a fully generational improvement scale is applied, then an arrow will appear to the right of the View button. Chose View table to display the mortality table and parameters as they were input. Clicking the View button itself will display the same as this first option. Choosing View table for an individual will yield another dialog box. Specify an age and a valuation year and click View, and ProAdmin will display the projected mortality for an individual who is that age in that valuation year. To produce the mortality rates that ProAdmin uses, be sure to increase the number of significant digits in Format values... after clicking the Options... button.
U.S. Internal Revenue Service guidance specifies the mortality tables to be used for determining lump sums under the Pension Protection Act of 2006 (PPA). Certain tables permissible or required in the regulations are static tables, meaning that generational projection is not applied. These static tables are updated by the IRS annually to reflect mortality improvements.
Select New/Dynamic to create a new dynamic mortality table.
Select if the IRS base rates and projection methodology should use the 2018 methodology (see 2018+ Dynamic Mortality) or the 2008 methodology (see 2018+ Dynamic Mortality).
Select the Blend type from the following three options:
- None. This produces a sex distinct pre/post commencement table similar to the Static Mortality (dynamic) tables.
- Pre/post combined (Small plan). This produces a sex distinct table similar to the Small Plan Combined Static Mortality (dynamic) tables.
- Unisex pre/post combined (417(e)). This produces a unisex table similar to the Applicable Mortality for 417(e) (dynamic) tables.
Select the Improvement scales as variable by calendar year. This example is the IRS 2018-2019+(MP16-17) Static Mortality (dynamic) table with an estimated MP-2018 improvement scale to calendar years 2020 and beyond.
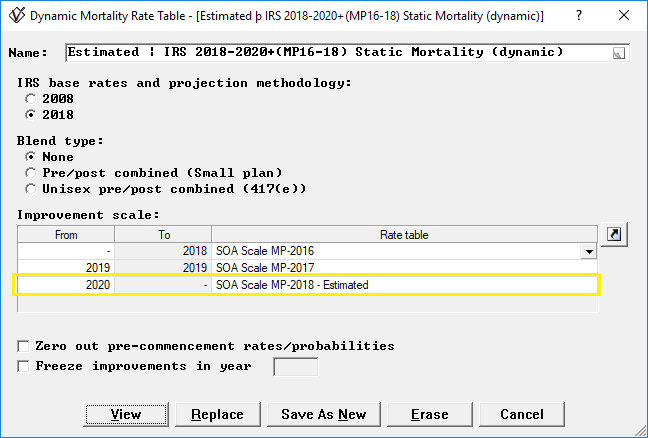
Check the Zero out pre-commencement rates/probabilities box if you wish to set the pre-commencement rates to zero (although ProAdmin only recognizes and uses post-commencement rates).
Check the Freeze improvements in year box if you wish to freeze the improvement rates in a particular calendar year. The improvement rates will stay the same for calendar years after the year you enter.
Current Applicable 417(e)
When attempting to view a dynamic mortality table, the dialog box asks What year would you like to view? Enter the desired calendar year in the parameter’s text box. If the dynamic table is also a 417(e) table, there is a subsequent option to Use the current applicable 417(e) mortality for year. Checking this box will swap the selected mortality table for the most recent available table containing the published rates for the selected year (or projection, if applicable). This is useful when checking mortality for objects that use a similar checkbox within their parameters.
Click View and ProAdmin will build the static rate table associated with that year and present it for you to print, view, or file.
- IRS Revenue Ruling 2007-67 is the table named “IRS 2008+ Applicable Mortality Table for 417(e) (dynamic)”
- IRS Notice 2017-60 is the table named “IRS 2018+ Applicable Mortality Table for 417(e) (dynamic)”
- IRS Notices 2018-02, 2019-26, 2019-67, 2020-85, and 2022-22 were each issued to update the applicable 417(e) mortality tables and the mortality improvement scales on which they were based for years 2019 through 2023. Each table in ProAdmin is named to reference 2018, the year the mortality development methodology changed, the year of the notice, and the mortality improvement scale applicable. For example, "IRS 2018-2019+(MP16-17) Applicable Mortality for 417(e) (dynamic)"
- IRS Notice 2023-73 is the table named "IRS 2024+ Applicable Mortality Table for 417(e) (dynamic)." The IRS changed the base mortality table this year as well as the mortality improvement scale. IRS Notice 2024-42 updated the applicable mortality table for 2025 without changing the base mortality nor the mortality improvement scale used in 2024. Accordingly, no new tables were added to ProAdmin for 2025.
If you reference any of the these tables in an Actuarial Equivalence definition for both Member and Beneficiary mortality and check the box for Use the current applicable mortality for 417(e), ProAdmin will generate the mortality rates for each annuity commencement date based on the plan years of that commencement date. ProAdmin will automatically anticipate the mortality improvements for future plan years as required under PPA without a need for the user to physically change the table each year when the new Revenue Ruling is issued. Thus for a commencement date based on the plan year of that commencement date beginning prior to 2018 ProAdmin will use IRS 2008+ Applicable Mortality Table for 417(e) (dynamic), during 2018 it will use IRS 2018+ Applicable Mortality Table for 417(e) (dynamic), during 2019 it will use IRS 2018-2019+ Applicable Mortality Table for 417(e) (dynamic), and so forth. For details on how these tables are generated please see the Technical Reference topic Dynamic Mortality.
Please note that in additional to the built-in options for freezing a mortality table "at its source", there are a few other options for controlling/limiting dynamic (and sometimes generational) mortality tables:
- The IgnoreDynmortTblsYr= setting in the[config} section of ProAdmin.ini allows you to control the dynamic mortality table year when testing an update to ProAdmin.
- The Dynamic Mortality Tables topic in the Projection Assumptions allows you to freeze dynamic mortality at the most recent published year.
- The Freeze mortality at date in field parameter in the Actuarial Equivalence and Annuity Factor components libraries allows you to freeze dynamic and generational mortality at a date, such as a participant's termination date, for that library's calculations.